8 batteries (Fixed Charging and Discharging Strategy, Fully Charged and Discharged.)
The first cycle measures the initial capacity: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 0.5C (1A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA) (also called CC-CV mode); resting for 5 minutes;
discharging to 2.5V with a constant current of 0.2C (0.4A).
For other cycles: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 2.0C (4A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A); resting for 5 minutes;
discharging at 1.0C (2A) until 2.5V; resting for 5 minutes.
15 batteries (Fixed Charging and Discharging Strategy, Fully Charged and Discharged.)
The first cycle measures the initial capacity: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 0.5C (1A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA); resting for 5 minutes;
discharging to 2.5V with a constant current of 0.2C (0.4A).
For other cycles: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 3.0C (6A), then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A);
resting for 5 minutes; discharging at 1.0C (2A) until 2.5V; resting for 5 minutes.
8 batteries (Variable Discharging Strategy, Fully Charged and Discharged.)
The first cycle measures the initial capacity: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 0.5C (1A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA);
resting for 5 minutes; discharging to 2.5V with a constant current of 0.2C (0.4A).
For other cycles: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 2.0C (4A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A);
resting for 5 minutes; discharging at x C to 2.5V (where x is cycled through values of {0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5}); resting for 5 minutes.
8 batteries (Variable Discharging Strategy, Fully Charged but not Fully Discharged.)
The first cycle measures the initial capacity: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 0.5C (1A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA);
resting for 5 minutes; discharging to 2.5V with a constant current of 0.2C (0.4A).
For other cycles: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 2.0C (4A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A); resting for 5 minutes;
discharging at a current of x C to 3.0V (where x is cycled through the values of {0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5}); resting for 5 minutes;
After each cycle, measuring the capacity by charging at a CC-CV mode with 2C (4A) to 4.2V, resting for 5 minutes,
and discharging at a current of 1C (2A) to 2.5V, then resting for 5 minutes.
8 batteries (Random walking discharging, Fully Charged but not Fully Discharged.)
For the first 20 cycles: charging is carried out at a constant current of 0.5C (1A) to 4.2V,
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA);
resting for 5 minutes; then discharging at a current of x A for y minutes
(where x is a random integer in the interval [2, 8] and y is a random integer in the interval [2, 6]),
stopping the discharge when the voltage drops to 3.0V to ensure safety; resting for 20 minutes.
Starting from cycle 21, the following operation is repeated: measuring the capacity once
(by charging at a CC-CV mode with 1C (2A) to 4.2V, resting for 5 minutes, and discharging at a current of 1C (2A) to 2.5V, then resting for 5 minutes),
and discharging randomly for 10 cycles (by charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 3.0C (6A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A); resting for 5 minutes;
then discharging at a current of x A for y minutes
(where x is a random integer in the interval [2, 8] and y is a random integer in the interval [2, 6]),
stopping the discharge when the voltage drops to 3.0V to ensure safety; resting for 10 minutes).
8 batteries (Simulate the charging and discharging strategy for a Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) satellite.)
The first cycle measures the initial capacity: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 0.5C (1A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.02C (40mA);
resting for 5 minutes; discharging to 2.5V with a constant current of 0.2C (0.4A).
For other cycles: Charging to 4.2V with a constant current of 2.0C (4A),
then maintaining the voltage unchanged until the current drops to 0.05C (0.1A), resting for 5 minutes,
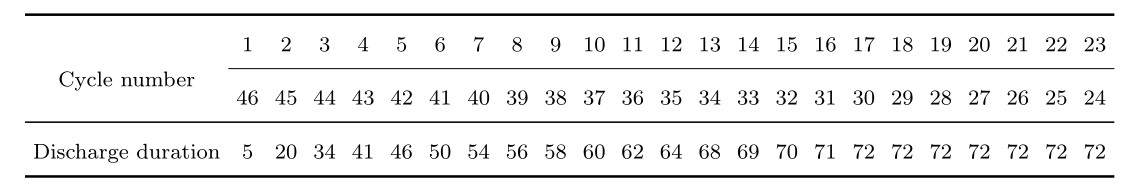
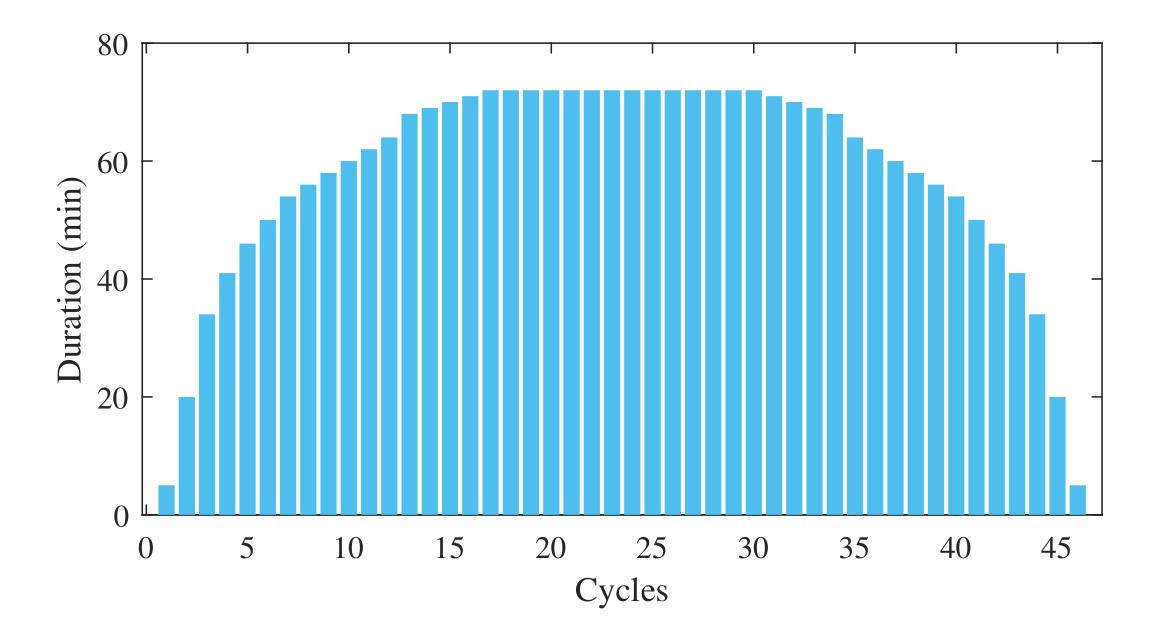
and then discharging at a constant current of 0.667C (1.334A) for a duration, as shown in Table and Figure.
The capacity is measured approximately every 5 cycles by charging at a CC-CV mode with 1C (2A) to 4.2V,
resting for 5 minutes, and discharging at a current of 0.5C (1A) to 2.5V.